|
||
|
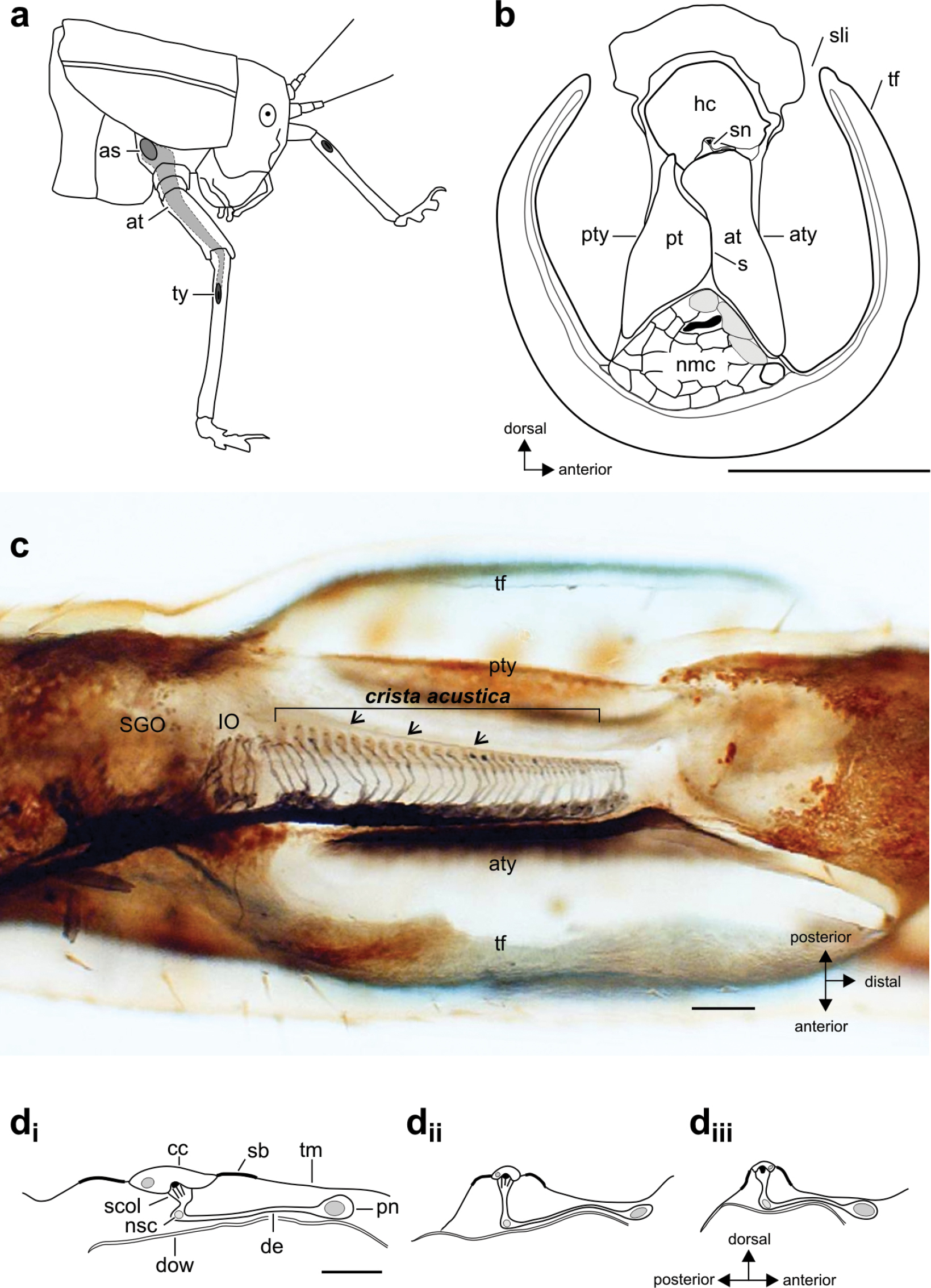
The auditory system of bushcrickets. a. Schematic of the acoustic trachea (at) from the acoustic spiracle (as) in the thorax into the foreleg with tympanal membranes (ty) in the proximal tibia; b. Transverse section of the tibia at the level of the tympana and crista acustica in Gampsocleis gratiosa; in Gampsocleis gratiosa; c. The sensory organs in the proximal tibia of the male Tettigonia viridissima. The dorsal cuticle has been removed after axonal tracing of the tympanal nerve with cobalt solution to stain sensory neurons of the subgenual organ (SGO), intermediate organ (IO) and crista acustica. The crista acustica is placed between the anterior tympanum (aty) and posterior tympanum (pty). The tympanal flaps (tf) cover the tympanal membranes. Arrows indicate the tectorial membrane; d. Morphological differences of sensory neurons along the crista acustica from G. gratiosa, showing the (di) third-most proximal, (dii) middle, and (diii) third-most distal sensillum. Abbreviations: at, anterior trachea; aty, anterior tympanum; cc, cap cell; de, dendrite; dow, dorsal tracheal wall; hc, haemolymph channel; IO, intermediate organ; nmc, nerve muscle channel; nsc, nucleus of scolopale cell; pn, perikarya of sensory neurons; pt, posterior trachea; pty, posterior tympanum; s, septum; sb, supporting band; scol, scolopale cap and rods; SGO, subgenual organ; sli, slit; sn, sensory neuron; tf, tympanal flap; tm, tectorial membrane. Scales: 500 µm (B), 100 µm (C), 50 µm (D). Figure a. reprinted from Strauß et al. 2014, with permission from John Wiley and Sons. b., d. redrawn from Lin et al. 1994, with permission from John Wiley and Sons. |